Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
When electrons gather on the surface of an object, such as a rubber balloon, and
move slightly in all directions, it is called
a. | direct current electricity | b. | alternating current
electricity | c. | static electricity | d. | an electric
discharge |
|
|
|
2.
|
The electroscope shown here is  a. | positively charged | b. | negatively charged | c. | neutral | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
3.
|
The following object is 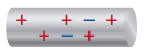 a. | a positively charged object | b. | a negatively charged object | c. | a neutral
object | d. | none of the above |
|
|
|
4.
|
Nylon is above polyester on the electrostatic series. Predict the resulting
charge of each object if a nylon rope came into contact with a polyester cloth.
a. | nylon rope: negative; polyester cloth: positive | b. | nylon rope:
negative; polyester cloth: negative | c. | nylon rope: positive; polyester cloth:
positive | d. | nylon rope: positive; polyester cloth: negative |
|
|
|
5.
|
All of the following are insulators, except
a. | iron | b. | ebonite | c. | pure
water | d. | wool |
|
|
|
6.
|
If metal rod X and metal rod Y come into contact with each other, what would be
the resulting charge on each rod?  a. | rod X: positive; rod Y: negative | b. | rod X: positive; rod Y:
positive | c. | rod X: negative; rod Y: negative | d. | rod X: negative; rod Y:
positive |
|
|
|
7.
|
If a material comes into contact with the sphere of a charged metal leaf
electroscope with raised leaves and the leaves of the electroscope fall, you can conclude that the
material is a(n)
a. | conductor | b. | insulator | c. | charged
object | d. | neutral object |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following devices make use of static electricity?
a. | dishwasher | b. | clothes dryer | c. | toaster
oven | d. | laser printer |
|
|
|
9.
|
If an atom has the same number of protons and electrons, it has what type of
charge?
a. | positive | b. | negative | c. | neutral | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
10.
|
The two objects shown here would 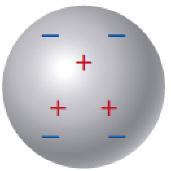 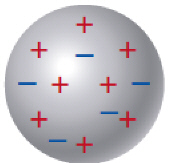 a. | attract each other | b. | repel each other | c. | neither attract nor
repel each other | d. | The interaction cannot be determined. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following is an atomic particle that moves from object to
object?
a. | proton | b. | electron | c. | neutron | d. | nucleus |
|
|
|
12.
|
Two neutral objects made of different materials coming into contact with each
other always results in two objects with
a. | like charges | b. | opposite charges | c. | neutral
charges | d. | positive charges |
|
|
|
13.
|
Dust collecting on a computer monitor is a result of
a. | charging by friction | b. | charging by conduction | c. | charging by
induction | d. | grounding |
|
|
|
14.
|
All of the following materials would be used to make a lightning rod,
except
a. | iron | b. | copper | c. | wood | d. | silver |
|
|
|
15.
|
What type of charge does the following atom have? 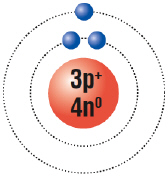 a. | positive | b. | negative | c. | neutral | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
16.
|
When one object exerts an electric force upon another object, the strength of
that force is dependent upon
a. | the distance between the two objects | b. | the amount of charge on each
object | c. | all of the above | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
17.
|
When a positively charged object is grounded,
a. | protons travel from the object into the ground until it is
neutral | b. | protons from the ground travel up to the object until it is
neutral | c. | electrons travel from the object into the ground until it is
neutral | d. | electrons from the ground travel up to the object until it is
neutral |
|
|
|
18.
|
What causes your hair to stick to a brush as it is being brushed?
a. | charging by friction | b. | charging by conduction | c. | charging by
induction | d. | grounding |
|
|
|
19.
|
For this object to become positively charged, which of the following would have
to occur?  a. | The object would have to gain a proton. | b. | The object would
have to lose a proton. | c. | The object would have to gain an
electron. | d. | The object would have to lose an electron. |
|
|
|
20.
|
When a negatively charged object and a neutral object are brought near each
other,
a. | the neutral object becomes negatively charged | b. | the neutral object
becomes positively charged | c. | the neutral object remains neutral, but the
side nearest the negatively charged object becomes temporarily negatively charged | d. | the neutral object
remains neutral, but the side nearest the negatively charged object becomes temporarily positively
charged |
|