Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The majority of Earth’s atmosphere is made up of what gas?
a. | argon | b. | carbon dioxide | c. | nitrogen | d. | oxygen |
|
|
|
2.
|
Earth’s average surface temperature is
a. | 10 °C | b. | 15 °C | c. | 20 °C | d. | 25 °C |
|
|
|
3.
|
The rocky outer shell of Earth is called the
a. | atmosphere | b. | biosphere | c. | hydrosphere | d. | lithosphere |
|
|
|
4.
|
Living organisms and their physical and chemical environment make up a(n)
a. | habitat | b. | ecosystem | c. | biome | d. | ecological
niche |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following correctly orders the components of an ecosystem from
simplest component to most complex component?
a. | organism, population, community, ecosystem | b. | organism, community,
population, ecosystem | c. | ecosystem, community, population,
organism | d. | community, population, organism, ecosystem |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following is an abiotic feature of a coniferous forest
ecosystem?
a. | usually in tropical latitudes | b. | contains many biting flies | c. | much of the
precipitation falls as snow | d. | small, temporary
ecosystem |
|
|
|
7.
|
An example of an artificial ecosystem is a(n)
a. | coral reef | b. | beaver pond | c. | urban
park | d. | rotting log |
|
|
|
8.
|
The form of energy that warms the atmosphere, evaporates water, and produces
winds is
a. | radiant energy | b. | light energy | c. | thermal
energy | d. | chemical energy |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following is an example of a consumer?
a. | green plants | b. | single-celled algae | c. | cyanobacteria | d. | humans |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following is a by-product of photosynthesis?
a. | oxygen | b. | water | c. | carbon
dioxide | d. | light energy |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following is a true statement regarding photosynthesis and cellular
respiration?
a. | Photosynthesis and cellular respiration both occur continuously. | b. | Cellular respiration
is a complementary reaction to photosynthesis. | c. | Cellular respiration and photosynthesis both
require light energy. | d. | Sugar and oxygen are products of both
photosynthesis and cellular respiration. |
|
|
|
12.
|
An animal that eats both plants and animals is called a(n)
a. | herbivore | b. | carnivore | c. | omnivore | d. | scavenger |
|
|
|
13.
|
A representation of energy, numbers, or biomass relationships in ecosystems is
called a(n)
a. | food chain | b. | trophic level | c. | food
web | d. | ecological pyramid |
|
|
|
14.
|
The following diagram is an example of a(n) 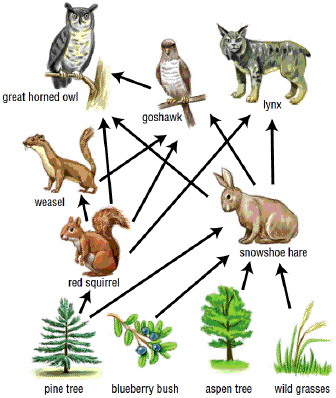 a. | ecological pyramid | b. | food chain | c. | food
web | d. | trophic level |
|
|
|
15.
|
Of the energy taken in by individuals at one trophic level, about what
percentage is passed on to individuals at the next level?
|
|
|
16.
|
The exchange that occurs between carbon dioxide in the atmosphere or dissolved
in water and photosynthesizing plants and micro-organisms is called the
a. | biogeochemical cycle | b. | carbon cycle | c. | nitrogen
cycle | d. | water cycle |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is an example of an abiotic factor that can influence a
species’ ability to survive?
a. | competition | b. | temperature | c. | predation | d. | mutualism |
|
|
|
18.
|
A tapeworm living in a dog is an example of
a. | predation | b. | mutualism | c. | parasitism | d. | commensalism |
|
|
|
19.
|
The maximum population size of a particular species that a given ecosystem can
sustain is called
a. | ecological niche | b. | limiting factor | c. | tolerance
range | d. | carrying capacity |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following is a biotic feature of the boreal forest biome in
Canada?
a. | warmer than the tundra | b. | contains pine martens | c. | contains
ferns | d. | changeable weather |
|